What is blockchain technology?
It’s a shared ledger for recording the history of transactions – that cannot be altered.
Why we need it?
Transactions take place every second — orders, payments, account tracking. Often, each participant has his own ledger — and, thus, his own version of the truth. Having multiple ledgers is a recipe for error, fraud and inefficiencies. The goal is to see a transaction end-to-end and reduce those vulnerabilities.
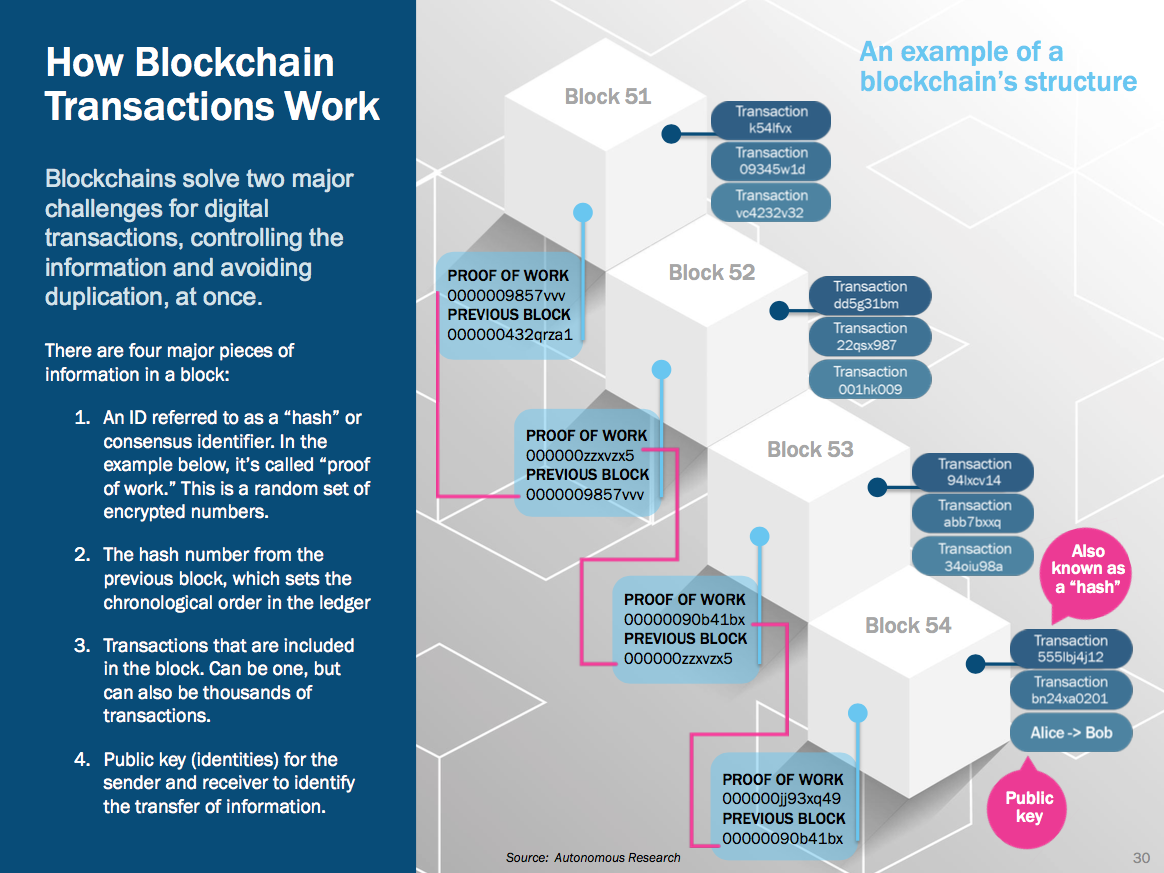
How blockchain works?
How Blockchain Helps Improve Supply Chain?
A key benefit of blockchain for supply chain networks is that it establishes a shared, secure record of information flows; a ‘shared version of events’ across networks for supply chain transactions, processes and partners.
We identified three major fields of action for our clients:
Traceability
The difficult and challenging process of traceability can be automated, simplified and accelerated by efficient use of Blockchain technology and corresponding electronic tracking technology (such as WiFi, BLE or RFID). In a not-so-far-away future, it could be possible to trace back every product to the origin of raw material used.
Smart Contracts
Another promising application for Blockchain lies in Smart Contracts, which are ‘electronic’ contracts based on automated actions that are triggered through predefined events. Such contracts can be used e.g. for automated execution of payments in case of an in-quality and on-time delivery. In a bigger picture, this scenario is an essential foundation for fully automated order calls, particularly in multi-stakeholder contracting.
Safe Transactions
A third potential usage for Blockchain technology lies in its capabilities for validating data: Blockchain allows one to follow and track the ‘journey’ of data, including a valid timestamp. This is useful in a wide variety of processes such as: Exchange of confidential business documents, transfer of shipping documents or orders and order confirmations.
Where do we see Blockchain Technology Use Cases in future Supply Chain Management?
Creating consistent traceability of goods will remain a major objective for future supply chains. To achieve transparent and reliable documentation of all transactions, end-to-end communication in supply chains must be taken to a new level of maturity. In reality, most networks already fail at the creation of communication or data exchange between the members as well as on legal questions about data sovereignty. For any questions, please give us a call.